Return to Portfolio Index Core Principles (map) Back to Core Principles of Professional Relationships
Previous standard = Parent/caregiver Community Partnerships (page 4) Practicums were at these three schools: First and Second Semester 2010
Learning Processes
Teachers know about learning processes and how to teach and implement
Example characteristics of the standards
Demonstrate an understanding of teaching and learning principles
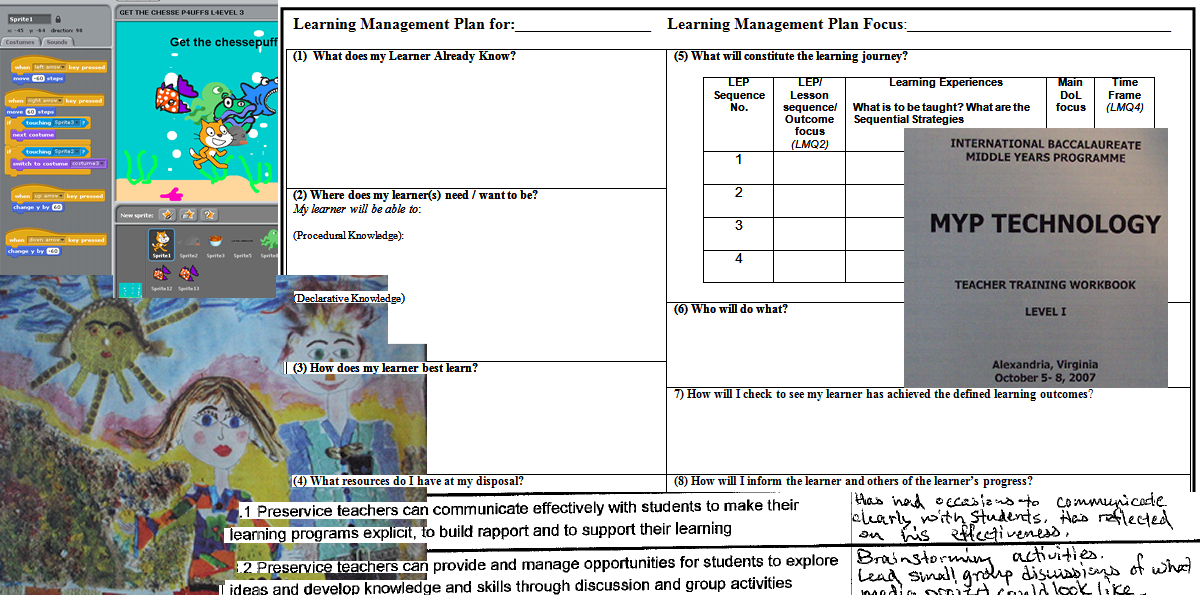
Demonstrate an ability to design and evaluate programs, locate and use various resources and structure learning opportunities to enthuse and engage learners

Further develop knowledge of contemporary learning theory and research, child and adolescent development and connections between pedagogy and practice
Understand the philosophy and structure of relevant curriculum frameworks
Understand the connections between pedagogy and assessment
Further develop knowledge of how assessment of and for learning can be structured to support the learner and influence learning
Demonstrate conceptual knowledge, confidence and personal skills related to literacy, numeracy and information and communication technologies (ICT)
The National Numeracy Review Report (May 2008), Chapter 3, points out the need to include particular groups of students such as indigenous, immigrants, and those with various learning behaviours and styles in embedding numeracy into the curriculum. Computer technology integrated across the curriculum can place practical learning such as with numeracy within a virtual environment that is easily accessible to students. Western mathematics derives from a western ‘world view’ which is largely about economics (Perso, 2003). This learning area is inline with the Melbourne Declaration on Educational Goals for Young Australian page 8., under The Educational Goals > Successful learners… "have the essential skills in literacy and numeracy and are creative and productive users of technology, especially ICT, as a foundation for success in all learning areas for Young Australians".